Everyone with a mole, skin tag or warts always wants to know how they can get rid of them. But few people want to go through any surgical procedure that is truly invasive. So which surgical procedure removes superficial skin lesions with scraping?
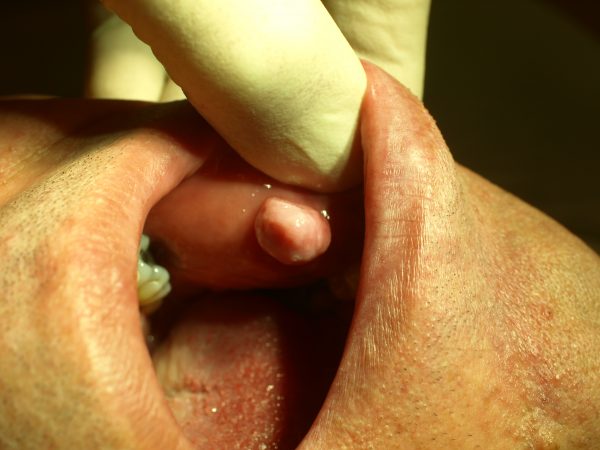
There are different procedures that are non-invasive for removing superficial skin lesions. Such procedures include cryotherapy, scissor excision and shave excision. But they don’t all involve scraping.
Table of Contents
Which Surgical Procedure Removes Superficial Skin Lesions with Scraping? – According to the Experts
Curettage, a medical term, is the surgical procedure that employs scraping to get rid of superficial skin lesions. In dermatological terms, it is actually called curettage and cautery, which is a form of electrosurgery. This procedure is done using a curette, a tool that looks much like a little spoon but with a really sharp edge.
The procedure is so minimally invasive, it is usually done in a doctor’s office, with you as an out-patient. And it doesn’t take a long time; you can be in and out to attend to other things on your to-do list.
Which Surgical Procedure Removes Superficial Skin Lesions with Scraping? – More Details
Before this procedure is used, it has to be ascertained that the skin condition is truly superficial and has no underlying disease or condition. If this is not exactly clear, it is best to visit your doctor.
This is because it could worsen the condition or accelerate its growth. It could also lead to infections. Not all superficial lesions are benign or harmless.
Skin lesions that are more malleable than the surrounding skin and are not painful can be scraped off using a curette.
Such lesions that are malleable and not painful include, but are not exclusive to, the following:
- Skin tags
- Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- Warts
- Actinic keratosis
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Angiomas
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Spider nevi
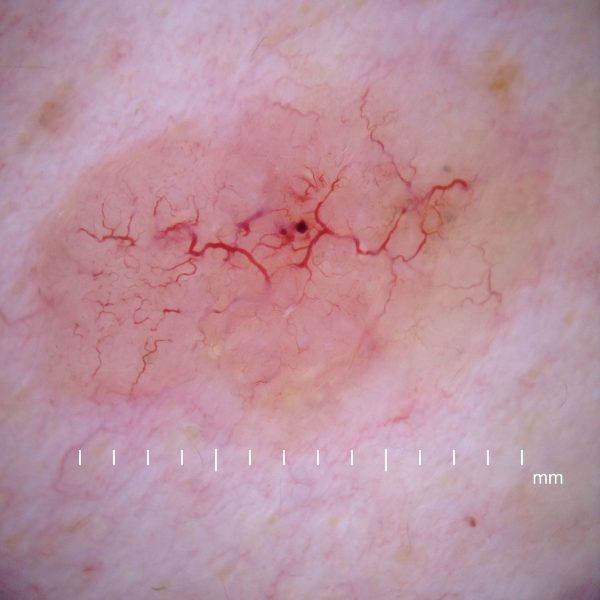
Which Surgical Procedure Removes Superficial Skin Lesions with Scraping? – Undergoing Curettage
What are the steps involved in removing superficial skin lesion with Curettage?
First, the skin surrounding the lesion has to be numbed with anesthetic, preferably a local one. This is to keep you from feeling any pain.
Second, the superficial lesion is scraped off using a curette.
Third, the top part of the open wound is cauterized with a needle or any other pointed metal instrument, to supply high-frequency current to it. What this does is to remove any other remnant tissue and to keep it from bleeding.
As an alternative to the electric current, aluminium chloride hexahydrate can also keep the wound from bleeding. It is good at coagulating blood and sealing tiny blood vessels.
Check out these interesting skincare product reviews/articles:
Neutrogena Naturals Purifying Daily Facial Cleanser – Detailed Review
Clearasil Gentle Prevention Daily Clean Wash – Detailed Review
How to Prevent Loose Skin after Gastric Bypass – In-depth Answer
How to Get Smooth Armpit Skin – Detailed Answer
Neutrogena Oil-free Pink Grapefruit Acne Face Wash – In-depth Review
Neutrogena Men Skin Clearing Acne Wash – Comprehensive Review
How to Take Care of the Wound after the Procedure
After the procedure and the dressing of the wound, there are home care tips for caring for the wound. When the anesthetic wears off, there will be some pain but that shouldn’t scare you. It is all part of the process.
How do you keep the wound from becoming infected?
To keep the wound from becoming infected and to speed up healing:
- Take some pain killers as prescribed, in order to ease off the pain.
- Keep from putting pressure on the wound and its surrounding area.
- Leave the dressing on the wound for as long as your doctor advises.
- Let the wound remain dry for about 2 days or as advised. After that time, you can clean and dry it gently.
- If it starts to bleed for any reason, gently apply some pressure on it using a clean cloth or towel for about 20 to 25 minutes. And if it keeps bleeding, see a doctor as soon as possible.
- If the open wound or the area around it becomes painful and red, it could be infected. See a doctor immediately.
The Risks Involved in Curettage
There is always the risk of scarring with curettage. This is because the curette has to get all parts of the lesion. That move could leave a slight scar at the spot.
Usually, the scars are not hideous because the lesions are small, to begin with. Your dermatologist can manage them so that their appearance would be barely there.
However, some people react differently to the healing process. While scars resulting from this procedure tend to be very small, theirs could be large and raised, instead of flat or depressed.
These types of scars have their own treatment to get rid of them but the thick skin from them may remain. But you could use creams or lotions, like the one below, to treat the scar if it isn’t so deep.
Another class of potential risks involved with curettage and cautery is damage to the nerves. Removing a lesion from a skin area with a large and intricate network of nerves could permanently or temporarily damage some nerves.
Which Surgical Procedure Removes Superficial Skin Lesions with Scraping? – Our Conclusion
Curettage is a safe procedure to get rid of skin lesions that remove from your looks or that are just unsightly. But if you are particular about scars, which the procedure is likely to leave, try another procedure that is less likely to leave any.
Which Surgical Procedure Removes Superficial Skin Lesions with Scraping? – Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Get Rid of Skin Lesions Yourself?
Here is a surefire yet painless way to get rid skin lesions yourself:
Take a wad of cotton wool and soak it in apple cider vinegar. Place it over the lesion and cover it with a bandage. Leave the bandage on for about 15 minutes, then take it off. Repeat this process every day for about 2 weeks.
Apple cider vinegar is highly acidic so its acid content will weaken the tissues holding the lesion in place. This will cause it to fall.
But before you embark on this process, ensure the lesion is benign. Be sure to check with your doctor so that you don’t touch a malignant lesion and compound the problem.
Which Term Means to Scrape Away Superficial Skin Layers?
The term for scraping away superficial skin layers is abrasion. It is also a term that represents scraping deep skin layers. In other words, abrasion is a wound, whether it is superficial or deep, caused when the skin comes roughly in contact with a rough object. It, therefore, comes in different degrees.
When the epidermis, which is the topmost skin layer, is abrased, there is usually no formation of scars. But when the abrasion goes to deep layers, the chances of scars forming are high.
A more serious type of abrasion, where all skin layers are affected, is named avulsion.
What Is the Most Superficial Skin Layer?
The most superficial skin layer is called the epidermis. It is this layer that keeps external pollutants from entering or invading the body.
The thickness of the epidermis varies, depending on the part of the body and the friction it encounters. While it is thickest on the soles of the feet and the palms of the hands, it is thinnest on the genitalia and eyelids.
Due to the fact it is the most visible layer, it gets the most care. If the epidermis is affected adversely, other layers of the skin will become affected in some way. In severe cases, organs of the body will get affected, too.
Why Is My Wound Healing Raised?
Your wound is healing raised because of the excessive production of collagen. Collagen helps to heal wounds and strengthen the areas affected by the injury. But this does not happen with everyone so it depends on the way your skin heals and your type of skin.
If your healing wound got inflamed or infected at some point, then the excess collagen production needed to boost healing is causing the raised scar. Also, if the wound was not stitched or is over a stress point like a joint, there will be a raised scar.
Sometimes, the raised scar will reduce in size after some time. But rest assured there is no underlying negative issue causing this.
Why Does My Healed Cut Still Hurt?
Your healed cut still hurts probably because the formerly damaged nerve endings are regenerating. When you initially had the wound, there was a chance the nerve endings in that area were destroyed in the process. So the cut did not hurt as much or stopped hurting after some time.
But now, you are starting to feel some pain where there is no longer a cut, only a scar. The reason is that your body is regenerating new nerve endings to replace the old ones. So you are feeling the pain of the tissues of the scar as the nerves grow back.
However, there is a chance the healed cut hurts because of a disease growing internally.
What Causes Wounds to Heal Slowly?
Causes of slowly healing wounds vary, ranging from infections, burns and trauma to more serious conditions like diabetes.
Age causes wounds to heal slowly. With age, almost everything slows down, including the speed of healing. The body takes longer to rejuvenate so healing takes longer.
Poor nutrition also affects the speed at which healing occurs. If you lack important nutrients that help to heal, then the process will be slow. Nutrients such as zinc are needed to make this happen.
Some medication such as some anti-inflammatory medication for arthritis and anticoagulants also interfere with the speed of healing.