If you’re dealing with skin discoloration after laser tattoo removal, this guide will help you manage and improve the appearance of your skin.
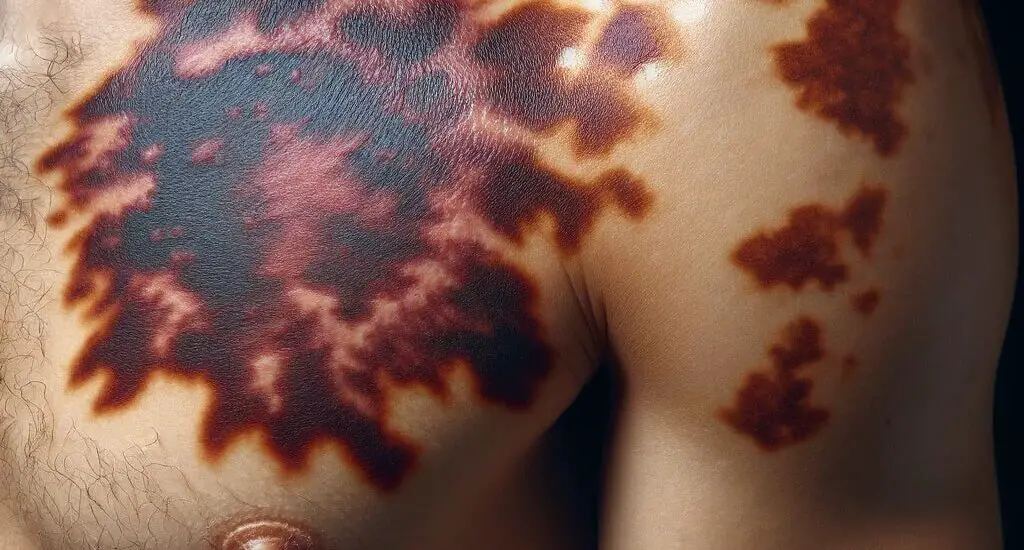

Table of Contents
Understanding Skin Discoloration After Laser Tattoo Removal
When a laser is used to remove a tattoo, it emits specific wavelengths of light that are absorbed by the tattoo ink. The absorption of light breaks down the ink into smaller particles. Your body’s immune system then removes these particles over time.
However, this process can sometimes affect melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which can either increase or decrease melanin production resulting in hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
It’s important to note that while any change in skin color can be alarming, not all discoloration is permanent. The type and extent of skin color change can vary based on your skin type, the color and location of your tattoo, the type of laser used, and the laser settings. While hyperpigmentation is more common in individuals with darker skin tones, hypopigmentation may occur in any skin type.
Moreover, the chances of skin discoloration can be influenced by factors such as sun exposure prior to treatment, the presence of certain substances in tattoo ink that may react unpredictably to laser treatment, and your body’s natural healing process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Prevent Skin Discoloration After Laser Tattoo Removal
The steps below will guide you on how to prevent skin discoloration after laser tattoo removal:
Step 1: Consult a Qualified Technician
It’s vital to choose a licensed and experienced laser tattoo removal professional. During the consultation, your skin type will be evaluated using the Fitzpatrick Scale, a numerical classification schema for human skin color.
An experienced technician will use this information to select the appropriate laser and settings, minimizing the risk of skin changes.
Step 2: Follow Pre-Treatment Advice
Your technician will provide you with a set of pre-treatment guidelines that you should follow carefully. This may include avoiding sun exposure for a certain period before the procedure to prevent tanning, which can increase the risk of hyperpigmentation.
It’s also recommended to cease the use of certain medications and skin products that can increase skin sensitivity.
Step 3: Understand the Laser Treatment Process
Understanding how the laser operates can help you better comprehend the associated risks. There are different types of lasers, and each type is suitable for different tattoo colors and skin types. Q-switched lasers, for example, are commonly used for tattoo removal and have a lower risk of skin discoloration.
During the treatment, short pulses target the ink without heating the surrounding tissue excessively, which can help prevent skin damage.
Step 4: Adhere to Post-Treatment Care
Following the procedure, it’s essential to take care of the treated area to encourage healing and reduce the risk of discoloration. This includes keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding picking at any scabs that form, applying prescribed ointments to avoid infections, and protecting the skin from sun exposure with a high-SPF sunscreen.
Step 5: Monitor Your Skin’s Healing
It’s normal for the skin to go through a range of colors and sensations as it heals. Keep an eye on the progress and report any concerns to your technician.
Documenting the healing process with photos can be helpful for both you and your provider to monitor the changes over time.
Managing Skin Discoloration After Laser Tattoo Removal if It Occurs
If you notice skin discoloration after laser tattoo removal, there are several options available for managing the condition. For mild cases of hyperpigmentation, using a high-SPF sunscreen can prevent the darkened areas from becoming more pronounced.
You can get this Aveeno Protect + Hydrate Body Sunscreen Lotion with SPF 60 from Walmart to protect your skin.
For more significant hyperpigmentation, products containing ingredients like hydroquinone can be used under the guidance of a dermatologist to fade dark spots. However, these products must be used cautiously, as overuse can cause skin irritation or worsening of the pigmentation.
For hypopigmentation, where the skin has lightened, there is often no quick fix, and the skin may take a longer time to return to its normal pigmentation. However, cosmetic cover-ups or self-tanners can be temporary solutions for camouflaging these areas.
Occasionally, more advanced treatments like chemical peels or further laser treatments may be recommended to stimulate melanin production in hypopigmented areas or reduce melanin in hyperpigmented spots. Always consult with a dermatologist or skin specialist before pursuing these treatments.
Remember, regardless of the type of skin discoloration you experience, patience is key. Skin healing can take time, and most changes will gradually improve or fade over time.