Dealing with white patches on skin after eczema can be perplexing and stressful. To alleviate your concerns, this article thoroughly covers the reasons behind these white patches, how they’re diagnosed, and the treatment options available.
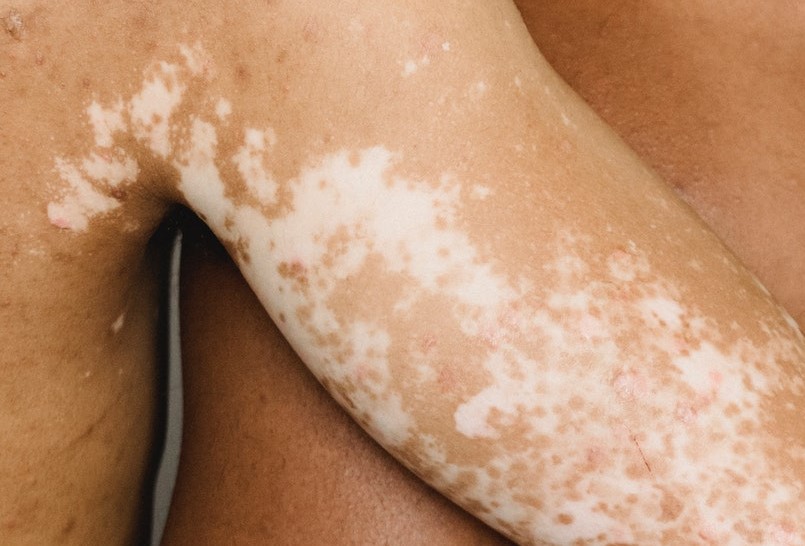
Table of Contents
Understanding the Relationship Between Eczema and White Patches
When you experience an eczema flare-up, the affected skin becomes inflamed, itchy, and red. Once the inflammation subsides and you start to heal, you may observe that the affected skin areas have lighter patches. These lighter or ‘white’ patches are a form of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Essentially, ‘post-inflammatory’ means ‘after inflammation,’ and ‘hypopigmentation’ indicates reduced skin color. It happens because the melanin-producing cells, known as melanocytes, become less active during the healing process.
According to a paper published by the National Institutes of Health, post-inflammatory hypopigmentation often occurs after skin conditions like eczema. It is your body’s response to inflammation and is generally not a cause for alarm.
Causes: Can Eczema Cause White Patches on Skin?
The short answer is yes, eczema can lead to white patches on the skin. As your skin heals from the inflammation and irritation caused by eczema, several factors can interfere with the skin’s normal pigmentation:
Medications: Topical treatments like steroids, commonly used to control eczema, can affect the melanocytes and lead to lighter skin patches.
Natural Healing Process: During the healing process, the affected skin may naturally produce less melanin, leading to areas of hypopigmentation.
DermNet NZ reports that such hypopigmentation is generally temporary and may resolve as the skin continues to heal and regenerate.
Diagnosis of White Patches on Skin After Eczema
If you notice white patches on skin after eczema flare-up, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. Typically, the dermatologist will perform a visual examination. They may also use a Wood’s lamp, a device that uses ultraviolet light, to get a closer look at the pigmentation changes.
A skin biopsy may be recommended to rule out other potential conditions such as vitiligo or fungal infections that also cause pigmentation changes.
We strongly recommend consulting a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment planning tailored to your specific needs.
Check out these other related articles…
Discoloration of Skin Due to Eczema: Comprehensive 411 Guide
Bumps on Skin From Eczema: A Comprehensive 411 Guide
Lines on Skin from Eczema: Comprehensive 411 Guide
Red Skin After Eczema: Your Complete Treatment Guide
Can Skin Recover From Eczema: The Ultimate Guide to Healing
Skin Peeling After Eczema Flare Up: Healing or Concern?
Does Skin Discoloration from Eczema Go Away? Detailed Answer
How to Get Rid of White Patches on Skin After Eczema
There are several treatment options for dealing with white patches caused by eczema, and they often depend on the extent and location of the hypopigmentation:
Topical Treatments: Creams containing ingredients like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can stimulate the melanocytes and help restore natural skin color. Always confirm with your healthcare provider before using any cream.
Light Therapy: Also known as phototherapy, this involves controlled exposure to UV rays under medical supervision. The treatment aims to stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin.
Laser Treatment: Targeted laser therapy can also be effective, though it is generally considered a last resort when other treatments fail.
A study in Science Direct supports the effectiveness of light therapy in treating post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prevention of White Patches on Skin After Eczema
The best way to prevent white patches after eczema is to manage your eczema effectively:
Mild Skincare Products: Use soaps, lotions, and laundry detergents that are hypoallergenic and free from irritants like perfumes and dyes.
Avoid Triggers: Common triggers include certain foods, stress, and environmental factors like pollen or dust. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help prevent eczema flare-ups and, consequently, white patches.
Follow Medical Advice: Adherence to your medication and skincare routine as advised by your healthcare provider can go a long way in controlling eczema and preventing pigmentation issues.